Snowflake: Cloud Data Platform Leader
Deep Dive into $SNOW: Valuation, Segment Growth, Key Metrics, Profitability, Expenses, Product Launches, Customer Acquisition, Financial Stability, SBC/Revenue, and Shareholder Dilution.
Snowflake: Company overview
About the Company
Snowflake, founded on July 23, 2012, is a cloud-based data storage and analytics company headquartered in Bozeman, Montana. The company provides a unified platform for storing, managing, and analyzing structured and semi-structured data across AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Mission
Snowflake aims to mobilize data through a single, integrated cloud-native platform, supporting seamless data sharing and collaboration across a multi-cloud infrastructure.
Sector
Snowflake operates in the rapidly expanding cloud data platform sector, specializing in data warehousing, data lakes, data engineering, and analytics solutions. Key competitors include Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Microsoft Azure Synapse.
Competitive Advantage
Snowflake’s cloud-native architecture features decoupled storage and compute, allowing independent scaling for optimized performance and cost efficiency. The platform’s elastic warehouse automatically scales workloads from 7XL to 100XL clusters, handling demand without downtime. Multi-cloud compatibility across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud further strengthens Snowflake’s market position against competitors.
Market Opportunity
Snowflake estimates its total addressable market (TAM) at $290 billion by 2027, growing at a 15% CAGR from 2022. The company holds 1.4% market share and projects annual revenue growth of at least 30% through 2029.
Valuation
After a significant drop, $SNOW is trading at a Forward EV/Sales multiple of 10.45—below 2022-2023 levels and significantly below the median of 17.8, near its historical lows.
$SNOW trades at a Forward P/E of 129.8. In 2024, under new CEO Sridhar Ramaswamy, the company significantly increased operating expenses, particularly in R&D, returning to an earlier stage of growth.
The EPS growth forecast for 2026 is 45.5%, with a 2026 PEG ratio of 2.8.
The PEG (Price/Earnings to Growth) ratio is a key tool for evaluating growth stocks, introduced by Peter Lynch.
PEG < 1: Undervalued – A ratio below 1 suggests the stock is undervalued. For example, if the P/E is 15 and earnings are expected to grow by 20%, the PEG would be 0.75, indicating a good buying opportunity.
PEG = 1: Fair Value – A PEG of 1 means the stock price matches its growth expectations, representing fair value.
PEG > 1: Overvalued – A PEG above 1 indicates the stock may be overvalued, as its price is higher than its projected growth rate, making it riskier.
Valuation comparison
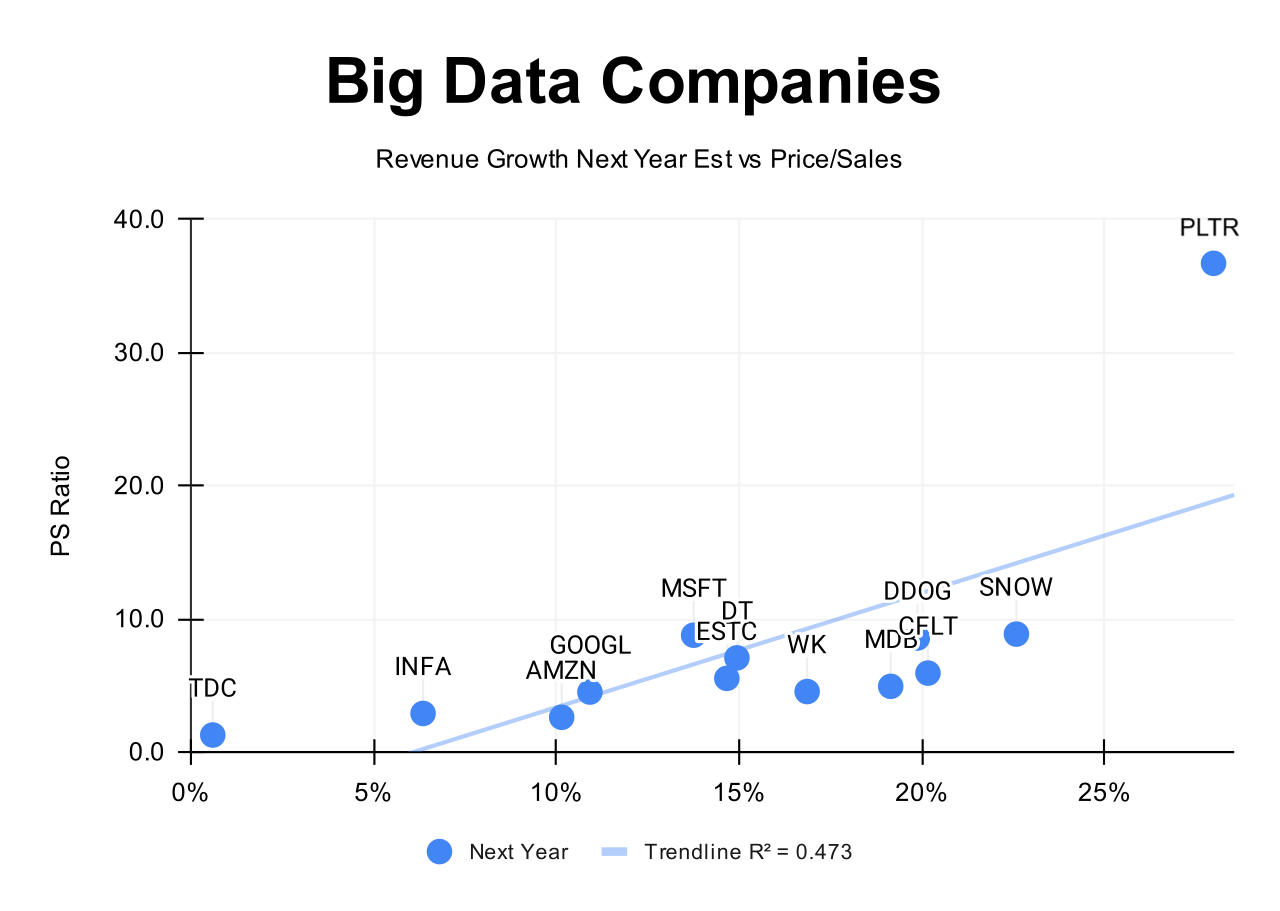
Analysts forecast $SNOW's revenue growth at +23% in 2025, one of the highest among the companies I am monitoring. Considering the 2025 revenue forecast, the valuation based on the P/S multiple appears undervalued compared to companies in the big data sector.
Analysts expect strong revenue growth, so let's examine the key metrics to determine whether these expectations are justified.
We'll evaluate the company's economic moat, which supports long-term revenue growth, analyze revenue trends and the forecast for the next quarter, and identify factors that could help the company exceed expectations and drive future growth.
We'll assess the performance of key segments, the launch of new products and updates, customer acquisition growth, key financial metrics, financial stability, and margin trends. Additionally, we'll review the SBC/Revenue ratio, shareholder dilution, and finally, draw conclusions.
Economic Moat
Snowflake has built a strong economic moat in cloud-based data warehousing and analytics, securing its competitive position and driving long-term revenue growth. Key factors reinforcing this moat include economies of scale, network effects, brand strength, intellectual property, and switching costs.
Economies of Scale
Snowflake’s cloud-native architecture and large customer base enable significant cost advantages. Fixed infrastructure and development costs are spread across 10,618+ customers, reducing per-user expenses. Scalability enhances margins and pricing power, strengthening Snowflake’s competitive edge.
Network Effects
Snowflake benefits from strong network effects. As more users adopt the platform, data-sharing capabilities expand, making the ecosystem more valuable. This self-reinforcing cycle increases customer stickiness, attracting new enterprise clients and making it difficult for competitors to replicate.
Brand Strength
Snowflake has established itself as a market leader in cloud data warehousing, known for high performance, scalability, and security. 800+ Forbes Global 2000 companies rely on Snowflake for mission-critical data operations, reinforcing its brand power and driving customer acquisition and retention.
Intellectual Property
Snowflake’s proprietary architecture, which decouples storage and compute, optimizes cost efficiency and performance. Multi-cloud compatibility across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud further differentiates Snowflake from traditional on-premise and single-cloud solutions, solidifying its technological advantage.
Switching Costs
Snowflake locks in customers through high switching costs. Transitioning to another provider requires downtime, retraining, and reconfiguration, creating operational risk. This complexity discourages migration, fostering long-term retention and recurring revenue growth.
Snowflake’s strong economic moat, built on scale, network effects, brand power, proprietary technology, and high switching costs, secures its leadership in cloud data solutions. As global data consumption accelerates, Snowflake remains well-positioned for sustained market expansion.
Revenue growth
However, $SNOW Snowflake's revenue growth has slowed from an exceptional >100% YoY post-IPO to +27% in Q4 2024. This slowdown is broadly seen across the software sector, yet Snowflake remains one of the fastest-growing companies.
RPO growth decelerated to +33.3% YoY, though it still outpaces revenue growth. Management attributes this slowdown to large customers consuming capacity faster than expected and shifting to on-demand purchases instead of early renewals. However, management expects these customers to sign larger contracts within six months.
Billings growth also slowed to +16.4% YoY, which is now below the revenue growth rate.
Considering the forecast for the next quarter, if the company beats its own guidance by 4.2%, which is its average beat over the last four quarters, Q1 revenue growth would reach 26.3%, signaling a slight deceleration in growth.
Segments and Main Products.
Snowflake's revenue primarily comes from two segments: Product and Professional Services.
The Product segment accounts for 95.6% of total revenue, driven by Snowflake’s core offerings, including data warehousing, data lakes, data engineering, data science, and secure data-sharing capabilities.
Professional Services and Other contribute around 4-5% of revenue, encompassing consulting, training, and implementation support to help customers optimize their use of Snowflake’s platform.
Key products include Snowpipe, which enables seamless real-time data ingestion from external cloud storage like Amazon S3 and Azure Blob.
Snowflake Marketplace facilitates verified data sharing and collaboration among organizations, offering datasets and services that meet quality and security standards.
The company's AI initiatives are integrated into its Cortex platform, which hosts leading AI models from OpenAI and Anthropic, enabling advanced analytics and AI-driven insights.
Snowflake also provides Native Apps through its Marketplace, allowing customers to deploy third-party solutions directly into their Snowflake instances for enhanced functionality.
The core platform delivers integrated cloud services for data warehousing, data lakes, data engineering, analytics, and secure data sharing, all built on scalable cloud infrastructure.
Main Products Performance in the Last Quarter
Cortex AI
Growth is accelerating, with 4,000+ customers using AI and machine-learning capabilities weekly. Snowflake is expanding AI offerings with Cortex Agents, providing automated orchestration for structured and unstructured data. Integration with OpenAI and Anthropic models strengthens Snowflake’s AI platform, enhancing retrieval, search, and automation. AI-driven data analytics is seeing strong adoption, but converting this into direct revenue impact remains a challenge.
Apache Iceberg
Iceberg adoption is expanding Snowflake’s addressable market by allowing enterprises to query and manage large-scale datasets without migration. Customer interest is turning into tangible revenue, with storage still accounting for ~11% of total revenue. Iceberg is creating new opportunities for data engineering and analytics workloads. Initial concerns over potential data movement out of Snowflake are now offset by the influx of new workloads.
Snowpark
Snowpark contributed 3% of FY ‘25 product revenue, reflecting strong enterprise adoption of Python, Java, and Scala-based data engineering. AI and machine-learning applications built on Snowpark are growing as enterprises adopt broader analytics capabilities. Snowflake is expanding functionality to simplify implementation. The challenge remains in deepening industry penetration beyond cloud-native companies.
Dynamic Tables
Dynamic Tables simplify real-time data processing and are driving significant adoption. Customers benefit from defining complex data transformations with simple SQL, eliminating the need for traditional ETL processes. Increased adoption is fueling Snowflake’s data engineering growth. Performance enhancements and expanded integrations are key areas of focus to sustain momentum.
Snowflake Marketplace
Marketplace plays a growing role in data collaboration, enabling enterprises to distribute and monetize data for AI training and analytics. Major customers such as Stripe, NTT, and Braze each maintain 160+ active data-sharing connections. Expanding the network effect and improving seamless integrations are priorities for growth. Marketplace is reinforcing Snowflake’s position as a central hub for enterprise data exchange.
Product innovations
Last quarter, $SNOW released several important updates and reported some achievements:
Over 400 new capabilities were launched in FY '25, more than double the previous year. Cortex Agents introduce automated data workflows, simplifying the deployment of AI-driven applications. Expanded partnerships with OpenAI and Anthropic integrate top-tier AI models while maintaining enterprise-grade security.
Snowflake Convert is now free, accelerating migrations from Oracle and Teradata. New connectors for SharePoint, Google Drive, Workday, and Slack enhance data ingestion and integration. Iceberg support is expanding, enabling new analytics workloads without data movement. Advancements in data-sharing continue to strengthen Snowflake’s ecosystem.
Snowflake appointed Mike Gannon as its new Chief Revenue Officer (CRO), effective March 14, 2025. Previously President of Americas Sales at VMware by Broadcom, Gannon will lead Snowflake’s revenue and go-to-market teams to drive its next phase of growth. He brings over a decade of experience in high-growth, competitive markets, with leadership roles at EMC Corporation and Isilon Systems.
Customers
$SNOW Snowflake added 541 total customers, reflecting +18% YoY growth, higher than Q4 of last year. The company also added 38 large customers with $1M+ ARR, achieving +27% YoY growth, accelerating from +25% in the previous quarter. While this addition is significantly higher than Q4 2023, it remains lower than in Q4 2022.
Customers Success Stories
Fiserv, a global financial technology provider, is transforming business intelligence using Snowflake’s platform. The company leverages Snowflake to create a robust analytics platform, giving clients real-time access to transaction data, market insights, and AI-driven decision-making. By using Snowflake’s architecture, Fiserv is enabling businesses to train AI models on financial data that was previously only accessible to large enterprises.
AstraZeneca is utilizing Snowflake to unify research data and accelerate drug discovery. By consolidating massive datasets within Snowflake, the company is optimizing its AI-driven clinical research, aiming to develop 20 new medicines by 2030. The efficiency of Snowflake’s AI-ready data platform is improving the speed and accuracy of pharmaceutical advancements.
State Street, managing 10% of the world’s financial assets, is using Snowflake’s AI and machine-learning capabilities to generate market insights. The ability to process and analyze financial data in real time is enhancing investment decision-making, reinforcing Snowflake’s role as a critical data infrastructure provider in capital markets.
Blue Yonder is driving AI-powered supply chain transformation with Snowflake, processing over 20 billion AI predictions daily. Retailers, manufacturers, and logistics companies use Snowflake’s scalable infrastructure to optimize inventory, delivery routes, and operational efficiency. The company’s ability to leverage AI-driven insights is creating new revenue streams for its clients.
Large Customer Wins
Snowflake continues to expand its enterprise footprint with major wins across multiple industries. ExxonMobil, Honeywell, and the London Stock Exchange Group have chosen Snowflake as a core component of their data infrastructure. These companies are investing in Snowflake to break down data silos, enhance collaboration, and drive AI-powered analytics at scale.
Fiserv, a leader in global payments, has integrated Snowflake’s AI-driven analytics into its core offerings, strengthening its competitive edge. Customers can now combine internal transaction data with market intelligence to gain deeper business insights, positioning Snowflake as an essential partner in the fintech space.
Stripe, NTT, and Braze each have over 160 active data-sharing connections within Snowflake, underscoring the platform’s growing importance in secure enterprise data collaboration. Snowflake’s ease of use and cost efficiency are driving large-scale adoption among technology leaders.
Retention
$SNOW Snowflake’s retention rate remains one of the highest in its class at 126% in Q4 2024, decreasing by 1 PP QoQ. The company calculates this metric based on data from the past two years, making it a lagging indicator for Snowflake.
Net new ARR
$SNOW Snowflake added $172 million in net new ARR, reflecting a +9% increase YoY. Q4 is seasonally a weaker quarter for the company, yet net new ARR additions set a record for Q4 over the past three years.
CAC Payback Period and RDI Score
$SNOW Snowflake’s return on S&M spending is 32.6, in line with Q4 of the previous year.
Snowflake is not a pure SaaS company but operates on a consumption-based model, making metrics like the CAC Payback Period and net new ARR more volatile compared to traditional SaaS companies.
The R&D Index (RDI Score) for Q4 stands at 1.26, slightly above the median of 1.2 for the SaaS companies I monitor but still strong and significantly above the industry median of 0.7. Snowflake has increased R&D spending, temporarily lowering its RDI Score, as the impact of these investments will be reflected in future revenue growth.
An RDI Score above 1.4 is considered best-in-class, while the industry median of 0.7 highlights the importance of efficient R&D investment.
Key Metrics
Two key components of $SNOW Snowflake’s economic moat are high switching costs and strong network effects.
Data sharing has steadily grown from 22% two years ago to 36% in Q3 2024 and remained at 36% in Q4 2024, reflecting sustained engagement. Q4 is a seasonally weaker quarter, and in Q4 2023, data sharing declined by 1 PPs QoQ, making stability at 36% a positive indicator.
This metric is crucial in highlighting Snowflake’s network effect, as higher data sharing enhances platform utility, attracting more customers and reinforcing Snowflake’s competitive edge.
$SNOW Snowflake added 98 new listings to its Marketplace in Q4 2024, reflecting a 26% YoY increase, though lower than the previous quarter. The slowdown is attributed to shifting enterprise data strategies and stricter partnership evaluations. Customers are focusing more on high-value datasets and AI-powered insights rather than general-purpose listings.
To address this, Snowflake is enhancing AI-driven capabilities, improving data discoverability, and refining revenue-sharing models. Marketplace activity is expected to reaccelerate in H2 FY 2026 as AI applications scale.
This metric highlights Snowflake’s expanding ecosystem and the growing adoption of its data-sharing platform.
Profitability
Over the past year, $SNOW Snowflake’s margins have changed:
• Gross Margin declined from 74.3% to 72.6%.
• Operating Margin slightly increased from 9.2% to 9.4%.
• FCF Margin improved from 41.9% to 42.1%.
Operating expenses
Over the past two years, $SNOW Snowflake has reduced operating expenses, with a significant decline in the last quarter. S&M expenses dropped from 38% in Q4 2024 to 28%, while G&A decreased from 8% to 5%. Meanwhile, R&D spending remained high at 18% of revenue, reflecting the company’s commitment to reinvesting in product development.
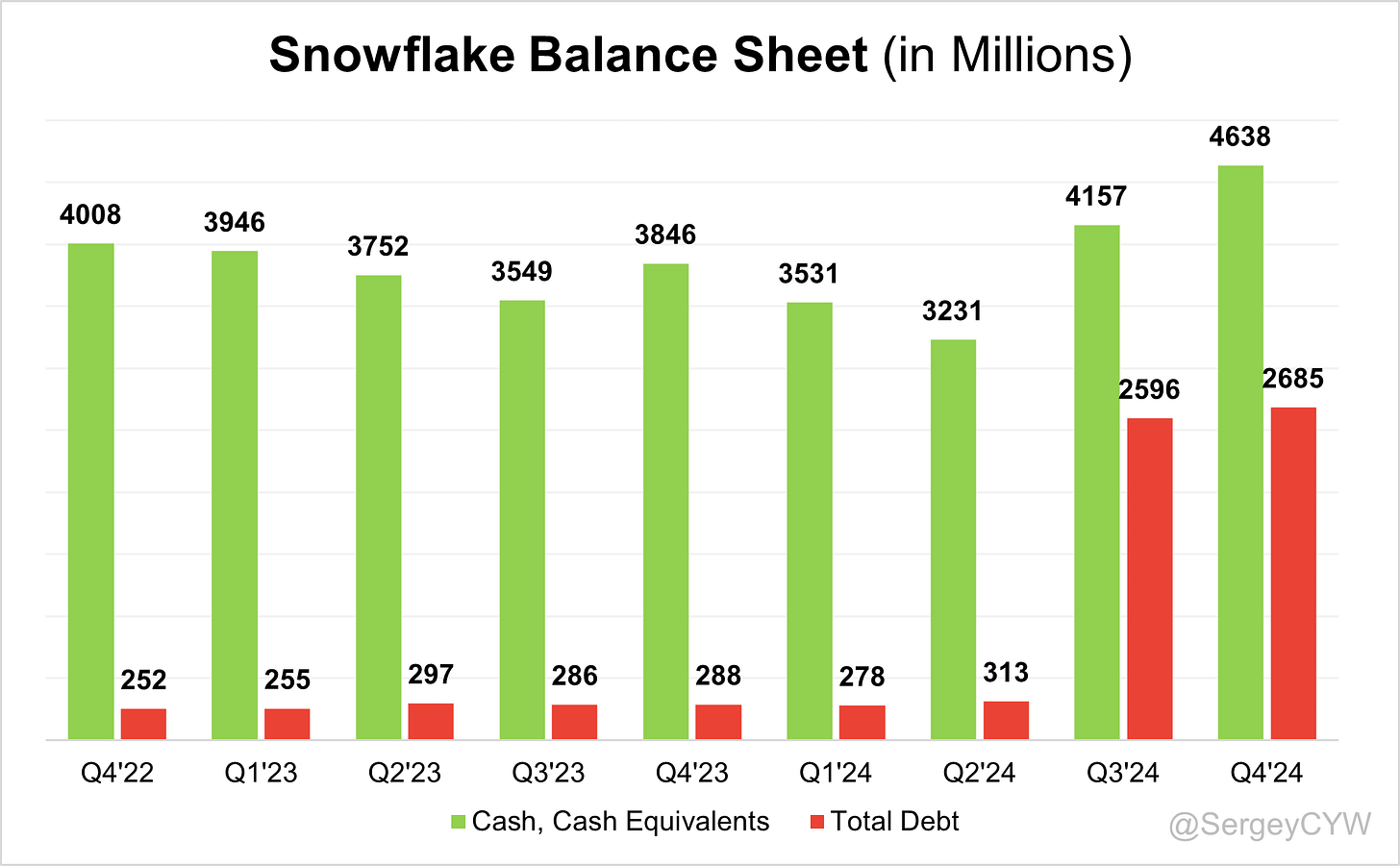
Balance Sheet
$SNOW Balance Sheet: Total debt stands at $2,686M. The company's debt increased in Q3 2024 due to the issuance of $2.3 billion in 0% convertible senior notes, split into $1.15 billion due in 2027 and $1.15 billion due in 2029. However, Snowflake holds $4,638M in cash and cash equivalents, keeping the balance sheet stable.
Dilution
$SNOW Shareholder Dilution: Snowflake's stock-based compensation (SBC) expenses increased in the last quarter to 46% of revenue, a very high level. However, for the full year 2024, SBC as a percentage of revenue decreased to 37% from 41%.
The company is actively repurchasing shares to offset dilution. Snowflake allocated $1.9 billion for stock buybacks, repurchasing 14.8 million shares at an average price of $130.87 per share. As a result, the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding increased by only 0.1% YoY.
Conclusion:
$SNOW Snowflake is strengthening its competitive position through product innovation and expanded collaboration with major cloud providers. Innovation has accelerated significantly under CEO Sridhar Ramaswamy.
Considering the projected revenue growth for 2025, the forward P/S ratio appears undervalued. Analysts expect strong revenue expansion. Growth has slightly slowed, but management anticipates acceleration in H2 2025, driven by Cortex AI, Iceberg, and Snowpark adoption, increased enterprise demand in financial services, healthcare, and supply chain, and new workloads in advertising, cybersecurity, and real-time analytics.
Leading Indicators
· RPO growth of +33.3% exceeds revenue growth.
· Record net new ARR was added in Q4, increasing +9% YoY.
· Strong customer growth, including large enterprise accounts.
While RPO growth has slowed, Snowflake operates on a consumption-based model, and some large customers are shifting to on-demand purchases instead of early renewals. This skews RPO data, meaning the slowdown is not necessarily a concern.
Key Indicators
· Net Dollar Retention (NDR) remains high for a SaaS company, though it declined slightly last quarter.
· CAC Payback Period worsened, but Q4 is a seasonally weak quarter.
· RDI Score is gradually declining but remains high compared to SaaS peers.
Snowflake’s economic moat, particularly its high switching costs, continues to strengthen. Data sharing is at 36%, significantly up from 23% over the past two years. The company reduced S&M and G&A expenses while reinvesting heavily in R&D, further reinforcing its competitive advantage.
SBC as a percentage of revenue remains high. I hope management takes control of this and reduces SBC levels moving forward.
In December 2024, I increased my position in $SNOW after the Q3 earnings report. It now represents 9.1% of my portfolio.