NVIDIA: Powering the Future of AI and Accelerated Computing
Deep Dive into $NVDA: Valuation, Segment Growth, Key Metrics, Profitability, Expenses, Product Launches, Customer Acquisition, Financial Stability, SBC/Revenue, and Shareholder Dilution.
Nvidia: Company overview
About NVIDIA
NVIDIA Corporation, founded in 1993, is a leading American multinational headquartered in Santa Clara, California. The company designs graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for high-performance computing and data science, and system-on-chip units (SoCs) for mobile and automotive markets. NVIDIA is a pioneer in accelerated computing and artificial intelligence (AI), with a market capitalization exceeding $2.3 trillion and annual revenue of $130.5 billion as of April 2025.
Company Mission
NVIDIA pioneered accelerated computing to tackle challenges no one else can solve. The company's work in AI and digital twins transforms the world's largest industries while profoundly impacting society. NVIDIA's mission centers on reshaping industry through data-center-scale offerings and accelerated computing solutions. The company maintains 8,700+ granted and pending patent applications worldwide and supports 6 million developers in the NVIDIA Developer Program.
Sector and Market Position
NVIDIA operates in the semiconductor industry within the broader information technology sector. The company reports business results through two primary segments: Compute and Networking and Graphics. Compute and Networking generated $116.1 billion in fiscal 2025, up 145% from the previous year, while Graphics delivered $14.3 billion, up 6% year-over-year. NVIDIA holds an 80.2% market share in discrete desktop GPUs as of Q2 2023. The company became the seventh public U.S. company valued at over $1 trillion in 2023 and briefly overtook Microsoft as the world's most valuable publicly traded company with a market capitalization exceeding $3.3 trillion.
Competitive Advantage
NVIDIA's competitive advantage lies in its advanced GPUs, which serve as the gold standard for AI processing. The company's GPUs power AI training and inference across data centers, autonomous vehicles, and AI research applications. NVIDIA's hardware offers superior performance and efficiency compared to competing solutions while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The company's CUDA software platform and API enables creation of massively parallel programs utilizing GPUs, deployed in supercomputing sites worldwide. NVIDIA's Blackwell architecture represents the latest breakthrough, with the company achieving billions of dollars in sales in its first quarter. The platform delivers up to 2x performance improvement over prior generations through innovations like DLSS 4 and Reflex 2 technology.
Total Addressable Market (TAM)
The company’s Total Addressable Market (TAM) is expanding rapidly. Its data center TAM is projected to surpass $1 trillion by 2028 and reach $1.7 trillion by 2035, fueled by the rise of generative AI, robotics, and edge computing. NVIDIA’s entry into the CPU market adds another $35 billion in TAM.
The broader data center market is expected to grow at a 15% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2024 onward. Within this, extreme parallel computing (EPC)—a strategic focus for NVIDIA—is projected to grow at a 23% CAGR, becoming the core of data center silicon investment by the mid-2030s. Meanwhile, the gaming GPU segment is forecasted to grow at a 21% CAGR, adding approximately $49 billion in revenue between 2023 and 2028.
Valuation
Looking at $NVDA Nvidia's valuation through the Forward EV/Sales multiple, it stands at 15.9, above median of 12.2, and significantly lower than the January 2025 peak, when the multiple reached 20, as well as the 2024 high, when it peaked at 25.
Powered by FinChat.io — get 15% off with affiliate link for Compounding Your Wealth readers.
$NVDA Nvidia is currently trading at a Forward P/E multiple of 29.2, which is slightly below the median of 33.8. At the beginning of 2024, the Forward P/E stood around 40. The current valuation is near the lows seen between 2020 and 2023, when the Forward P/E bottomed at approximately 20.
The EPS growth forecast for 2026 is 28.3%, with a P/E of 32 and a PEG ratio of 1.1.
The EPS growth forecast for 2027 is 18.1%, with a P/E of 25 and a PEG ratio of 1.4.
Powered by FinChat.io — get 15% off with affiliate link for Compounding Your Wealth readers.
The PEG (Price/Earnings to Growth) ratio is a key tool for evaluating growth stocks, introduced by Peter Lynch.
PEG < 1: Undervalued – A ratio below 1 suggests the stock is undervalued. For example, if the P/E is 15 and earnings are expected to grow by 20%, the PEG would be 0.75, indicating a good buying opportunity.
PEG = 1: Fair Value – A PEG of 1 means the stock price matches its growth expectations, representing fair value.
PEG > 1: Overvalued – A PEG above 1 indicates the stock may be overvalued, as its price is higher than its projected growth rate, making it riskier.
$NVDA Nvidia is trading at an EV/FCF multiple of 31.1, which is slightly below the median of 35.4.
Powered by FinChat.io — get 15% off with affiliate link for Compounding Your Wealth readers.
Valuation comparison
Analysts forecast +54.3% revenue growth for $NVDA in 2025 and +25.3% in 2026. Considering this projection, the valuation based on the EV/S multiple seems reasonable compared to other semiconductor companies.
Economic Moat
Economic Moats enable companies to remain stable during crises and support long-term revenue growth.
Economies of Scale
NVIDIA's economies of scale represent one of its strongest competitive advantages, driven by massive revenue growth and market dominance. The company achieved $44.1 billion in revenue for Q1 fiscal 2026, up 69% year-over-year, demonstrating unprecedented scale in the semiconductor industry. NVIDIA holds a commanding 90% market share in the AI GPU market, allowing it to spread R&D costs across enormous production volumes. This scale advantage enables the company to invest heavily in cutting-edge manufacturing processes and secure premium access to TSMC's advanced fabrication capabilities, while competitors struggle to match these investments. The company's $500 billion commitment to US AI infrastructure over four years further reinforces its scale advantages through vertical integration and supply chain control.
Network Effect
NVIDIA's network effect centers around its CUDA software ecosystem, which has become the industry standard for AI workloads and parallel computing. The platform supports over 6 million developers in the NVIDIA Developer Program, creating powerful network effects as more developers build applications that attract more users to NVIDIA hardware. The company's first-mover advantage in AI computing, established with CUDA's launch in 2006, has created a self-reinforcing cycle where developer adoption drives hardware demand, which in turn attracts more developers. More than 40,000 companies currently use NVIDIA AI technology, while the platform powers all 30 of the top 30 autonomous vehicle data centers, demonstrating the strength of its ecosystem network effects.
Brand Strength
NVIDIA has built exceptional brand equity that has become synonymous with high-performance computing and AI leadership. The company's brand strength stems from decades of innovation and consistent delivery of cutting-edge products, making it the preferred choice for both gamers and AI professionals. NVIDIA's position as one of the "Magnificent Seven" tech stocks alongside Amazon, Apple, and Meta reflects its premium brand status in the technology sector. The brand's association with AI leadership is reinforced by powering models from OpenAI, Google, and Meta with its H100 and A100 chips, creating a halo effect that attracts enterprise customers. The company's GeForce brand maintains strong recognition among 200 million gamers and creators, providing diversified brand strength across multiple market segments.
Intellectual Property
NVIDIA's intellectual property portfolio provides substantial competitive protection, though it faces some emerging challenges. The company maintains 8,700+ granted and pending patent applications worldwide, covering critical technologies in GPU architecture, AI acceleration, and parallel computing. However, NVIDIA currently faces a significant patent infringement lawsuit from Xockets Inc., which alleges that NVIDIA's Data Processing Unit (DPU) technology infringes on Xockets' patents and seeks both damages and an injunction. Despite this legal challenge, NVIDIA's extensive IP portfolio in GPU design, CUDA architecture, and AI-specific optimizations continues to provide meaningful barriers to entry for competitors. The company's continuous innovation in areas like ray tracing, DLSS technology, and Blackwell architecture generates new IP assets that strengthen its competitive position.
Switching Costs
NVIDIA has created substantial switching costs through its integrated hardware-software ecosystem, particularly via CUDA platform lock-in. Developers who build applications using CUDA face significant costs and time investments to port their code to competing platforms like AMD's ROCm or Intel's oneAPI. The company's full-stack AI solutions, including DGX systems, Grace Hopper processors, and DRIVE platforms, create additional switching costs as customers integrate these technologies into their infrastructure. Enterprise customers using NVIDIA's data center solutions face substantial migration costs due to optimized software stacks, trained personnel, and integrated workflows. The Omniverse platform and AI development tools further increase switching costs by creating dependencies on NVIDIA's proprietary technologies and formats.
Nvidia's moat is built on very strong economies of scale, driven by its dominant 90% share in the AI GPU market and massive quarterly revenue of $44.1B, alongside privileged access to TSMC's advanced manufacturing. It benefits from a strong network effect, with over 6 million developers on the CUDA platform and 40,000+ companies using its AI technologies, creating a powerful ecosystem lock-in. The brand is a major asset, positioning Nvidia as a premium name among the "Magnificent Seven" and the engine behind leading AI models and gaming platforms. While its intellectual property base of 8,700+ patents provides a moat, it's somewhat moderate due to ongoing legal challenges like the Xockets case. Most importantly, switching costs are very strong, thanks to the deep integration of Nvidia’s CUDA-based full-stack solutions, making it extremely difficult for enterprises to migrate away.
Revenue growth
$NVDA Nvidia's revenue growth was an incredible 262% in Q1 2024 and decreased to an equally remarkable 69% in Q1 2025. The primary growth driver is the Data Center segment, whose revenue is outpacing overall revenue growth.
Considering the forecast for the next quarter, if the company exceeds its own expectations by 2.5% as it did in Q1, the Q2 growth would be 53.5%, indicating a slowdown in revenue growth. However, it’s important to note that such extremely high revenue growth is unsustainable, and a slowdown is to be expected.
Segments and Main Products
NVIDIA operates through two primary business segments. The Compute and Networking segment dominates company operations, while the Graphics segment serves specialized markets with premium solutions.
Data Center
NVIDIA's business is led by its Data Center segment. This includes AI and high-performance computing GPUs like the H100 and A100, as well as software offerings such as CUDA, AI Enterprise, and DGX Cloud. NVIDIA's data center products support AI training, inference, and cloud workloads across major hyperscalers.
Gaming
The Gaming segment accounted for 8.7% of revenue in FY2025. Powered by the GeForce RTX series, this segment remains a leader in consumer graphics with features like ray tracing and DLSS. NVIDIA continues to outperform competitors including AMD's Radeon and Intel's Arc.
Professional Visualization
Professional Visualization made up 1.44% of FY2025 revenue. The segment includes RTX professional GPUs, used in architecture, healthcare, and film production. These products support CAD, 3D modeling, and complex simulations across aerospace, automotive, and medical fields.
Automotive
The Automotive segment contributed 1.3% of revenue. It includes the DRIVE platform, which delivers hardware and software for autonomous driving and infotainment systems. NVIDIA’s solutions process sensor data in real time to support safe and responsive self-driving functionality.
OEM and Other
OEM and Other was the smallest segment at 0.3% of revenue. It includes legacy GPUs, custom embedded AI solutions, and Tegra processors for mobile and gaming consoles. NVIDIA's focus has shifted toward data center and AI acceleration, which now drive most of its revenue and growth.
Main Products Performance in the Last Quarter
$NVDA Nvidia revenue by segment: Data Center revenue has increased from 60% of total revenue in Q1 2023 to 89% in the most recent quarter, becoming the largest contributor to overall revenue.
While Data Center revenue growth has slowed from an extraordinary +427% YoY in Q1 2024 to +73% this quarter, the growth rate remains exceptionally high and continues to be the primary driver of Nvidia’s overall revenue expansion.
The Automotive segment posted strong growth at +72% YoY, but it still accounts for only 1.3% of total revenue.
The most important contributor to $NVDA Nvidia's overall revenue growth is the Data Center segment, which reported 73% YoY revenue growth. The key question is whether the company can stabilize Data Center revenue growth, and at what level this growth needs to settle to justify Nvidia’s current valuation based on its existing multiples.
The second-largest contributor to $NVDA Nvidia’s overall revenue has been the Gaming segment, though its share has declined significantly from 30% two years ago to just 8.5%. In the most recent quarter, the segment reported a +42% YoY increase in revenue, accelerating from negative -11% growth in Q4 2024.
Data Center
Revenue hit $39 billion, up 73% year-over-year, driven by AI factory buildouts and surging inference demand. China revenue declined significantly due to new H20 export controls, resulting in $4.5 billion inventory write-down and $2.5 billion in unshipped orders. Customers like Microsoft are deploying thousands of Blackwell GPUs weekly. Despite China setbacks, global demand from sovereign cloud projects in Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Taiwan offset regional weakness. Export policy remains a critical challenge going forward.
Blackwell Growth
Blackwell ramped faster than any prior NVIDIA product. It contributed nearly 70% of data center compute revenue in Q1. GB200 NBL72 racks are now generally available. Top hyperscalers are deploying 72,000 Blackwell GPUs per week. Microsoft and OpenAI are scaling deployments to hundreds of thousands of units. Sampling for GB300 began in early Q2; production starts later this quarter. GB300 brings 50% more HBM and 50% higher FP4 inference compute vs GB200. NVIDIA maintains a tight annual cadence roadmap through 2028.
Dynamo: Inference Optimization
Blackwell delivered 30x higher inference throughput in MLPerf benchmarks vs H200. Inference speed for reasoning models improved 1.5x in one month. Customers like Capital One saw 5x latency reduction, and Cisco boosted code assistant accuracy by 40% using Nexmo microservices. New models like Deepseeker One and Llama NemoTron are driving exponential token generation. NVIDIA is supplying infrastructure for startups and hyperscalers processing over 100 trillion tokens per quarter. Inference is becoming the dominant AI workload.
Gaming
Gaming revenue reached $3.8 billion, up 48% sequentially and 42% YoY, setting a record. RTX 5060 and 5060 Ti launched at $299, doubling frame rates. New laptops with Copilot+ integration and Blackwell architecture are boosting adoption. Nintendo Switch 2 will use NVIDIA’s custom RTX GPUs with DLSS, bringing next-gen performance to 150M+ console base. AI PCs are driving demand among gamers and creators.
Professional Visualization
Revenue came in at $509 million, flat sequentially, up 19% YoY. Tariff uncertainty impacted system sales. Demand for AI workstations remains strong. Sequential growth is expected in Q2. NVIDIA launched DGX Spark and DGX Station—desktop form-factor AI supercomputers delivering up to 20 petaflops. DGX Spark available Q3; DGX Station ships later this year.
Automotive
Automotive revenue was $567 million, down 1% sequentially, but up 72% YoY. Growth driven by NEV demand and self-driving ramp across customers. Production with Mercedes-Benz has started. NVIDIA’s Isaac Groot and Cosmo World Foundation models are enabling robotic innovation in partners like Agility Robotics, Boston Dynamics, and GE Healthcare. GE is now using NVIDIA AI to power robotic imaging and surgical systems.
Robotics
NVIDIA launched Isaac Groot N1, the first open customizable foundation model for humanoid robots. Cosmos foundation models are now integrated by major robotics developers. Isaac platform powers simulation, training, and deployment. NVIDIA sees robotics as an industrial-scale opportunity, projecting hundreds of thousands of robotic factories and billions of robots in development. AI factory buildouts will support this trajectory.
OEM
NVIDIA expanded AI PC offerings with new GeForce RTX 5060 GPUs in desktops and laptops. Laptops start at $1,099. AI PC installed base now exceeds 100 million users. Partnerships with Microsoft bring Copilot+ AI features to RTX-powered systems. New OEM wins include Yum Brands, planning to roll out AI across 61,000 restaurants.
Product and Innovation Updates
Blackwell product line expanded with GB200 in full ramp and GB300 sampling. Networking grew 64% QoQ to $5 billion, driven by adoption of NVLink and SpectrumX. SpectrumX is now generating $8B annualized revenue, with new wins at Google Cloud and Meta. NVIDIA introduced NVLink Fusion to enable third-party ASIC and CPU makers like MediaTek and Qualcomm to integrate directly with NVIDIA platforms. Switches featuring silicon photonics will scale networks to millions of GPUs.
New AI microservices (Nexmo, NIMS), open reasoning models (Deepseeker One, Llama NemoTron), and enterprise platforms (RTX Pro, DGX Spark, DGX Station) are broadening vertical and horizontal reach.
Revenue by Region
The United States accounts for 47% of total revenue, making it $NVDA Nvidia’s largest market, with revenue growing +87% YoY in Q1.
China contributes 12% of total revenue and grew +122% YoY, with a significant acceleration in Q4.
Taiwan accounts for 15%, growth accelerates to +64% YoY growth rate.
Other Countries make up 24%, with revenue growing +54% YoY.
Revenue growth in China is outpacing Nvidia’s overall revenue growth in Q1.
Market Leader
NVIDIA has achieved unprecedented market leadership across multiple semiconductor segments, with Gartner officially recognizing the company as the global semiconductor market leader for the first time in 2024. The company captured 11.7% of the global semiconductor market share, surpassing longtime leaders Samsung Electronics and Intel.
Gartner significantly upgraded its estimates of NVIDIA's performance. The analyst firm now projects NVIDIA will maintain its leadership position, driven by marked increase in demand for discrete GPUs serving as the primary choice for AI workloads in data centers. The global semiconductor industry reached $655.9 billion in 2024, growing 21% year-over-year, with NVIDIA's dominance attributed to massive AI infrastructure buildout and 73.4% increase in memory revenue.
Mizuho Securities estimates NVIDIA holds between 70% and 95% market share in the AI chip sector. Dominance is built around its flagship H100 GPUs and the CUDA software ecosystem, which together create high switching costs and deep customer dependency. This foundation secures NVIDIA's leadership across AI training and inference workloads.
Customer Success Stories
Microsoft's Azure AI, powered by tens of thousands of NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, processed over 100 trillion tokens in Q1, marking a 5x year-over-year increase in inference volume. This represents a significant shift in AI compute demand from training to inference, driven by the adoption of reasoning models.
Capital One achieved a 5x reduction in latency for its agentic chatbot by integrating NVIDIA’s Dynamo. Cisco reported a 40% increase in model accuracy and a 10x improvement in response time in its code assistant by leveraging Nexmo microservices. Shell’s custom LLM trained on NVIDIA’s Nexmo improved accuracy by 30%.
Startups in the inference segment, utilizing B200 GPUs, tripled token throughput, driving higher monetization rates for high-value reasoning models like Deepseeker One. These results are backed by the MLPerf benchmark, where GB200 NBL72 delivered a 30x increase in inference throughput versus the H200 baseline on the Llama 3.1 benchmark.
In manufacturing, TSMC used Omniverse to save months in fab design. Foxconn accelerated simulations by 150x, and Pegatron reduced defects by 67%. These performance boosts underscore Omniverse’s enterprise-grade utility across industrial digital twins and automation.
In gaming, NVIDIA reported record revenue of $3.8 billion, supported by the launch of GeForce RTX 5060 and 5060 Ti, which double frame rates and reduce latency. The Nintendo Switch 2 now features next-gen custom RTX GPUs with DLSS, a landmark integration in console gaming.
Strategic Partnerships
Microsoft, OpenAI, and Google remain core partners, with Microsoft ramping toward hundreds of thousands of GB200 units. NVIDIA's hardware now forms the backbone of Azure's AI Foundry and OpenAI services, reinforcing NVIDIA’s position as the compute engine of generative and reasoning AI.
NVIDIA’s sovereign AI strategy is accelerating. The company is deploying nearly 100 AI factories globally, doubling both the number of sites and the average GPU count per factory year over year. Partnerships in Saudi Arabia and the UAE include multi-gigawatt projects, while the first national AI factories are under development in Taiwan and Sweden.
In the U.S. onshoring effort, Foxconn and Wistron are building AI supercomputer plants in Houston and Fort Worth, respectively. TSMC is constructing six fabs and two packaging plants in Arizona for NVIDIA chip production, with volume readiness expected by year-end. NVIDIA has made multi-year purchase commitments, anchoring its strategy to build a chip-to-supercomputer supply chain in America.
The networking portfolio saw substantial traction. Spectrum X now annualizes over $8 billion in revenue, with Google Cloud and Meta joining existing adopters like Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, and CoreWeave. NVLink shipments exceeded $1 billion in Q1, marking its emergence as a critical scale-up interconnect platform. The debut of NVLink Fusion enables direct ecosystem integration with ASIC and CPU providers like MediaTek, Qualcomm, and Alchip.
In enterprise AI, NVIDIA launched RTX Pro, DGX Spark, and DGX Station, each designed to modernize the $500 billion global IT infrastructure. Partners like Accenture, Cadence, and Deloitte are building on NVIDIA’s reasoning AI stack to transform enterprise workflows and productivity.
Automotive partnerships are expanding with GM and Mercedes-Benz, using NVIDIA’s full-stack AI solutions to develop next-gen vehicles and autonomous capabilities. Isaac Groot and Cosmos World are being integrated by robotics firms such as Agility Robotics, XPEN Robotics, and Boston Dynamics, with GE Healthcare deploying Isaac for robotic imaging and surgical systems.
China Export Restrictions and Challenges
The April 9, 2025 U.S. export controls immediately halted NVIDIA’s sales of H20 GPUs to China, despite prior approval. NVIDIA recorded $4.6B in Q1 FY26 H20 revenue but could not ship $2.5B in additional orders. A $4.5B inventory and purchase obligation write-down followed, partially offset by component reuse.
The China AI accelerator market, valued at ~$50B, is now largely inaccessible. Q2 FY26 guidance reflects an $8B revenue loss from the ban. No compliant alternative products are currently available or approved. Hopper cannot be modified further, limiting future access.
CEO Jensen Huang warned that U.S. restrictions are accelerating China's AI independence. Models like DeepSeq and QN are gaining global traction, strengthening non-U.S. AI stacks and eroding American leadership in AI infrastructure.
NVIDIA is scaling U.S. manufacturing, backing TSMC’s 6 fabs in Arizona and Foxconn’s Houston AI supercomputer plant. These moves support supply chain resilience, align with U.S. reshoring policy, and reduce dependence on volatile trade regions through long-term procurement commitments.
Profitability
Over the past year, $NVDA Nvidia has experienced changes in its margins and profitability:
– Gross Margin decreased from 78.3% to 60.5%.
– EBIT Margin decreased from 64.9% to 48.7%.
– Free Cash Flow (FCF) Margin declined from 57.3% to 59.5%.
– Net Margin declined from 57.1% to 42.6%.
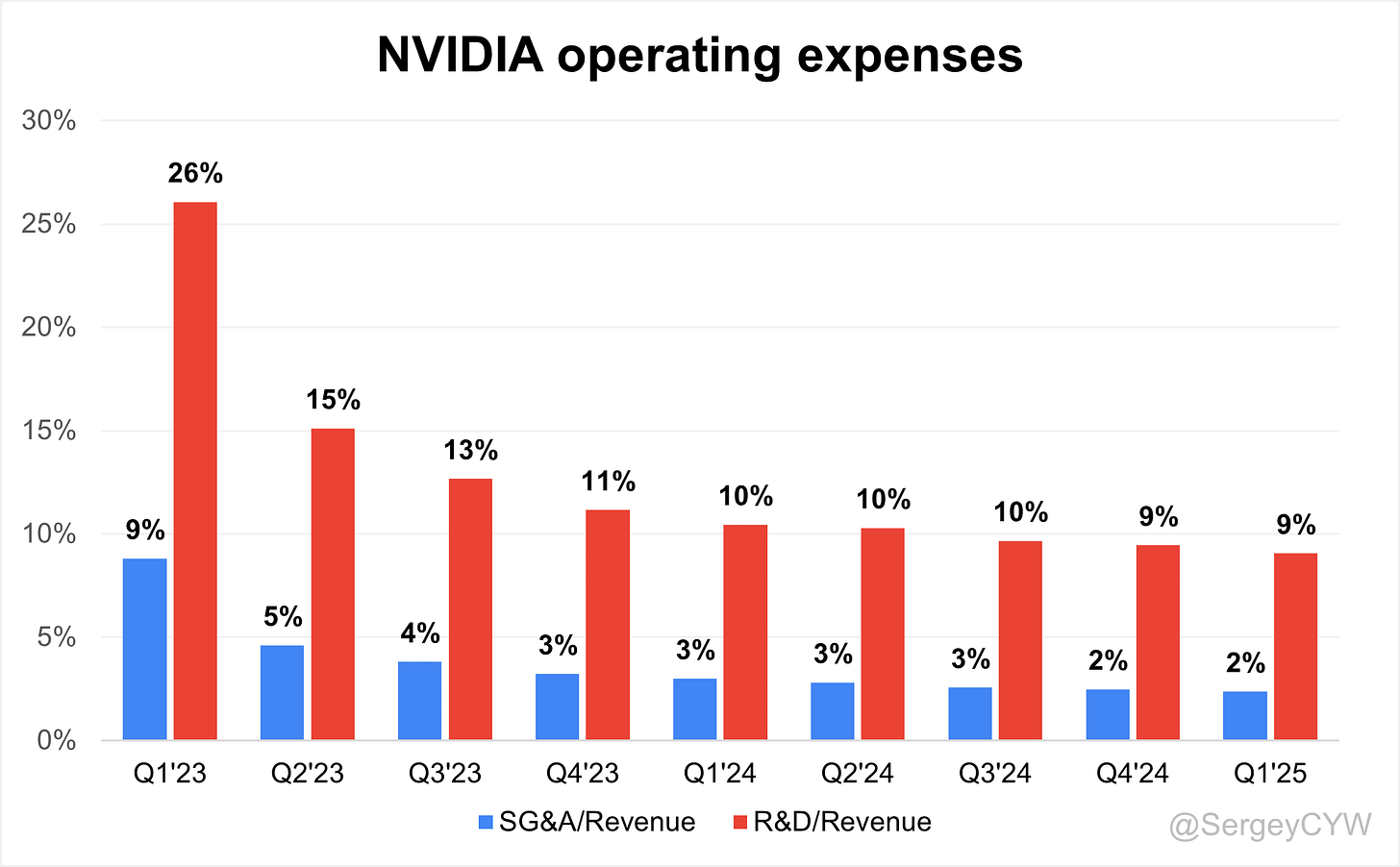
Operating expenses
Operating expenses have gradually decreased. Notably, $NVDA Nvidia spends more on R&D than on S&M and G&A combined, enabling the company to continuously improve its products and expand market share. R&D expenses remain high at 9% of revenue, while SG&A expenses have declined to 2%.
Balance Sheet
$NVDA Balance Sheet: Total debt stands at $10.3B, while Nvidia holds $53.7B in cash and cash equivalents, exceeding total debt and ensuring a healthy balance sheet.
Dilution
$NVDA Shareholder Dilution: Nvidia’s stock-based compensation (SBC) expenses declined in the last quarter, reaching 3% of revenue.
Shareholder dilution remains under control, as the weighted-average number of basic common shares outstanding decreased by 0.7% YoY, due to the company actively repurchasing its shares.
NVIDIA returned a total of $14.3 billion to shareholders during the first quarter of fiscal 2026. This represents the largest quarterly capital return in the company’s history.
Conclusion
$NVDA Nvidia has established itself as a highly innovative leader in the chipmaking industry. The company has effectively capitalized on the widespread adoption of AI technologies, with the launch of ChatGPT-4 serving as a major catalyst for explosive growth in its Data Center segment.
Revenue growth remains exceptionally strong at +69% YoY, with the Data Center segment growing +73% YoY, outpacing total revenue and acting as the primary growth engine.
However, growth is gradually decelerating. If Nvidia beats its Q2 forecast by the same margin as in Q1 (which was just +2.5%, the lowest beat in the past two years compared to +7.9% in Q3 2024), Q2 growth would reach approximately +53.5%.
Analysts forecast +54.3% revenue growth in 2025 and +25.3% in 2026. Expectations remain high, which makes it increasingly difficult for the company to continue outperforming. Forecast beats have been steadily shrinking: +7.9% in Q3 2024, +4.9%, and down to +2.5% in Q1 2025.
Nvidia is a cyclical business, and Data Center revenue growth is slowing, although it's worth noting that this particular cycle has been very long-lasting. The company is actively working to extend it by launching new products. The Auto segment posted an impressive +72% YoY growth in Q1, though it still represents just 1.3% of total revenue.
Valuation multiples like Forward P/E and EV/FCF are slightly below the median but are gradually increasing. However, the Forward EV/Sales is already above the median. The rise in multiples is largely due to declining operating and net profit margins. The net profit margin dropped from 57% in Q1 2024 to 42% in Q1 2025, though it remains extremely high for a chipmaker.
A key question is whether Nvidia can maintain its leadership and high margins, which will depend in part on continued demand for microchips. On the demand side, Q1 saw increased CAPEX from major tech companies, indicating strong ongoing demand.
The PEG ratio, despite high revenue growth, has increased relative to last quarter’s valuation: it's 1.1 for 2026 and 1.4 for 2027, reflecting expected margin compression—an assumption that appears reasonable.
Nvidia remains the clear market leader, but there are concerns about new competitors entering the space and the possibility that the AI demand cycle may peak, putting pressure on margins. This trend is already visible in Q1, where:
Gross margin declined -17.8 percentage points YoY
Operating margin fell -16.2 percentage points
Net margin dropped -14.5 percentage points
Another challenge is U.S. export restrictions on certain Nvidia chips, along with tariffs. In response and to improve supply chain resilience, Nvidia is scaling U.S. manufacturing, supporting TSMC’s 6 fabs in Arizona and Foxconn’s AI supercomputer plant in Houston.
Investors should closely monitor CAPEX trends from major tech players like $META, $MSFT, $GOOGL, and $AMZN, as they signal ongoing chip demand and potential for the current cycle to continue. Also worth watching are Nvidia’s upcoming product launches for AI and Data Center workloads, and the Auto segment, which—despite its small current share—shows strong growth potential.
Thank you for reading!
Follow me for more frequent updates on X/Twitter and Threads, and on LinkedIn. For visual infographics, check out Instagram, and for portfolio changes, follow me on SavvyTrader.
Disclaimer: This earnings review is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or trading advice.














NVIDIA... always a killer company! Thanks for the write up