MongoDB: Gaining Ground in the $96B Database Market with Scalable Cloud and AI-Driven Innovation
Deep Dive into $MDB: Valuation, Segment Growth, Key Metrics, Profitability, Expenses, Product Launches, Customer Acquisition, Financial Stability, SBC/Revenue, and Shareholder Dilution.
MongoDB: Company overview
About MongoDB
MongoDB, Inc. is a developer data platform company founded in 2007 and headquartered in New York City. The company offers a document-oriented database platform built for flexibility and scalability. MongoDB went public on NASDAQ in October 2017, raising $192 million at an initial valuation of $1.6 billion. As of 2025, the company employs 5,558 people and has a market capitalization of $16.03 billion. Revenue comes primarily from subscription services (74%), while professional services contribute the remaining 26%. Key products include MongoDB Atlas (cloud database-as-a-service), MongoDB Enterprise Advanced (self-managed commercial version), and Community Server (open-source offering).
Company Mission
MongoDB’s mission is to empower developers to build innovative applications using flexible, scalable database technology. The company promotes a software- and data-centric approach to solving modern application challenges. MongoDB is committed to sustainability and customer outcomes, backed by $349.7 million in R&D investment and a 92% customer retention rate.
Sector and Market Position
MongoDB operates in the database management systems (DBMS) market, with strong positioning in the NoSQL and cloud segments. It holds 8.14% of the global DBMS market. Within NoSQL, MongoDB commands 22.3% market share and captures 15.7% of the cloud database market. The company serves over 47,500 customers across key verticals: Technology (38%), Financial Services (22%), Retail (15%), Healthcare (12%), and Other (13%). In fiscal year 2025, MongoDB reported $2.01 billion in revenue but posted a net loss of $129.07 million.
Competitive Advantage
MongoDB’s core strength lies in its flexible document-based model, holding 26% share of the NoSQL market. Its distributed database architecture enables 100,000+ read and 50,000+ write operations per second. MongoDB Atlas, its cloud platform, offers recurring revenue and multi-cloud support across AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. The company's vector search is tightly integrated with its operational database, enabling AI-enabled applications. The platform has been downloaded 60 million+ times and is supported by a community of 12,500 active contributors.
Total Addressable Market (TAM)
MongoDB’s TAM for database management is estimated at $96 billion by 2025. The DBaaS market is projected to grow at a 20% CAGR through 2028, expected to represent 77% of the entire DBMS market by then—driving significant opportunity for MongoDB Atlas. The operational database segment alone is valued at $45 billion, and the cloud database market is projected to reach $72.9 billion by 2028. With a growing focus on AI and the acquisition of Voyage AI in February 2025, MongoDB is positioning itself to lead in AI-powered database innovation.
Valuation
$MDB MongoDB is trading at a Forward EV/Sales multiple of 5.8, which is significantly below the median of 14.56.
It is also below the 2019 low of 10.2 and the 2020 low of 9.5.
$MDB MongoDB is trading at a Forward P/E of 70.3, with revenue growth of +19.7% YoY in the last quarter.
The EPS growth forecast for 2026 is +27.9%, with a Forward P/E of 58.5, resulting in a 2026 PEG ratio of 2.1.
Looking ahead to 2027, the EPS growth forecast is +15.5%, with a P/E of 45.7 and a 2026 PEG ratio of 2.9.
The PEG (Price/Earnings to Growth) ratio is a key tool for evaluating growth stocks, introduced by Peter Lynch.
PEG < 1: Undervalued – A ratio below 1 suggests the stock is undervalued. For example, if the P/E is 15 and earnings are expected to grow by 20%, the PEG would be 0.75, indicating a good buying opportunity.
PEG = 1: Fair Value – A PEG of 1 means the stock price matches its growth expectations, representing fair value.
PEG > 1: Overvalued – A PEG above 1 indicates the stock may be overvalued, as its price is higher than its projected growth rate, making it riskier.
Valuation comparison
Analysts' revenue growth forecast for $MDB in 2026 is +19.3%. Considering this forecast, the valuation based on the PS multiple appears undervalued when compared to other companies in the Big Data sector.
Analysts expect solid revenue growth, so let's examine the key metrics to determine whether these expectations are justified.
We'll evaluate the company's economic moat, which supports long-term revenue growth, analyze revenue trends and the forecast for next quarter, and identify key factors that could help the company exceed expectations and sustain future growth.
We'll assess the performance of key segments, the launch of new products and updates, customer acquisition growth, key financial metrics, financial stability, and margin trends.
Additionally, we'll review the SBC/Revenue ratio, shareholder dilution, and finally, draw conclusions on the company's outlook.
Economic Moat
Economic Moats enable companies to remain stable during crises and support long-term revenue growth.
Economies of Scale
MongoDB benefits from moderate economies of scale as it expands its enterprise footprint and global infrastructure. Its cloud platform, MongoDB Atlas, operates across 85+ global cloud regions, supporting multi-cloud deployments on AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. With a growing customer base of 35,000+ enterprise customers, the company is able to spread infrastructure costs more efficiently. Technologies like independent shard scaling allow customers to optimize resource usage by scaling individual shards under heavy traffic. While MongoDB's cost efficiency improves with scale, economies of scale are not the company’s strongest moat compared to other factors.
Network Effect
MongoDB exhibits a strong network effect driven by its developer ecosystem. The platform supports a community of over 2 million registered developers, with 35,000+ GitHub stars and 500+ core contributors. This widespread adoption fuels platform improvements and reinforces a virtuous cycle—more users mean more tools, integrations, and expertise. In the NoSQL segment, MongoDB holds 31.7% market share, amplifying this effect. The open-source foundation encourages collaboration, making MongoDB more valuable as usage increases.
Brand
MongoDB has built a leading brand in the NoSQL database market, where it commands a 31.7% share as of 2023. Known for flexibility, scalability, and developer-friendly architecture, MongoDB’s document model accommodates dynamic data without predefined schemas—ideal for modern applications. Strong brand recognition translated into 29% YoY revenue growth, reaching $1.29 billion in FY2024. The company’s reputation continues to drive enterprise adoption and customer loyalty.
Intellectual Property
MongoDB maintains a moderate intellectual property moat, with 89 global patents, 69 granted, and 97% active. In 2018, the company transitioned from the open-source AGPL license to Server Side Public License (SSPL) to restrict unauthorized cloud usage. Co-founder Eliot Horowitz holds 30 patents, contributing significantly to the IP portfolio. While not vast, MongoDB’s licensing strategy strengthens its position by limiting platform misuse by major cloud providers.
Switching Costs
MongoDB’s switching costs are exceptionally high, forming its most durable moat. Migrating from MongoDB requires extensive data migration, application rewrites, and testing, especially for enterprise clients. The platform's document-oriented architecture creates significant integration depth within applications. Features like sharding, which distributes data across multiple servers, increase migration complexity. Enterprise customization demands a longer onboarding process, but this deep integration boosts customer lifetime value and reduces churn. Even Morningstar highlights MongoDB’s “significant switching costs” with its installed base.
MongoDB's moat is driven by strong network effects, brand strength, and very strong switching costs, securing its leadership in the database market and supporting long-term growth.
Revenue growth
$MDB MongoDB's revenue growth has significantly slowed to +19.7% YoY.
However, based on the forecast for the next quarter, if the company exceeds guidance by 5.7%, as it did in Q4, Q1 revenue growth could reach 24.0%, indicating a potential acceleration in revenue growth.
RPO and Billings growth have slowed, reaching +26.5% and +17.0% YoY, respectively.
Still, it's worth noting that RPO growth remains higher than revenue growth.
It’s important to highlight that MongoDB operates on a consumption-based model, rather than a traditional subscription-based SaaS model—making its revenue growth significantly more volatile compared to typical SaaS peers.
Segments and Main Products.
MongoDB's revenue is primarily divided into two segments: Subscription and Services. The Subscription segment generated $217.87 million in Q3 2022, representing 96% of total revenue, while Services contributed $9.02 million, accounting for the remaining 4%. Subscription revenue has shown strong growth, increasing by 50% year-over-year from Q3 2021 to Q3 2022.
MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas, the company's multi-cloud database-as-a-service offering, is MongoDB's flagship product, representing 71% of total revenue for Q4 2025 and growing at 24% year-over-year. Atlas operates across AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure, providing a fully managed cloud database solution with integrated services.
MongoDB Enterprise Advanced is the self-managed commercial offering, accounting for 24% of subscription revenue. Enterprise Advanced provides advanced security features, 24/7 support, and includes the MongoDB Ops Manager tool for monitoring, alerts, and performance analysis. Unlike Atlas, Enterprise Advanced requires manual updates and on-premises installation.
MongoDB Community Server is the free, open-source version with limited functionality, ideal for testing and learning. It has been downloaded over 155 million times since February 2009 and serves as an entry point for potential customers to experience MongoDB's core capabilities before upgrading to paid versions.
MongoDB's product portfolio extends beyond core database offerings to include specialized tools like Atlas Search for building search experiences, Vector Search for semantic search using vector embeddings, Stream Processing for handling complex event data, and Data API for HTTPS-based data access. Additional tools include Charts for data visualization, Data Federation for cross-platform querying, and various connectors for integration with Kafka, Spark, and BI tools.
Main Products Performance in the Last Quarter
Atlas
Atlas revenue reached $389.4M, up 24% YoY, and now accounts for 71% of total revenue. Growth was driven by strong new workload acquisition and improved cohort contribution from fiscal 2025. Consumption trends remained stable YoY in Q4, despite seasonally slower usage over the holidays. Management expects Atlas consumption growth to remain stable in FY26, supported by a larger volume of enterprise workloads and increased sales productivity. Atlas customer count rose to 53,100, up from 46,300 YoY.
Vector Search
Vector Search continues to see expanding usage within GenAI workloads. Customers like Swisscom deployed Atlas to power RAG applications using Vector Search to extract relevant context from unstructured data. MongoDB has integrated Vector Search directly into the operational database, reducing complexity for developers. Innovations in quantization significantly reduced storage costs and improved performance, positioning Vector Search as a core element in AI-driven use cases. This functionality is expected to be a competitive advantage as AI applications move from experimentation to production.
MongoDB 8.0
MongoDB 8.0 is central to the company’s application modernization push. Focus is on Java apps running on Oracle, where MongoDB combines AI tooling, agents, and delivery teams to migrate legacy workloads. The success of a major modernization for a large European ISV is now scaling to their broader application estate. Management believes AI-assisted modernization will contribute materially to new business growth by FY27. FY26 will focus on scaling pilots into more customer engagements.
Stream Processing
Stream processing was not directly highlighted in the Q4 earnings call, suggesting it remains a nascent or low-priority segment relative to Vector Search and app modernization. No new metrics or updates were provided, implying limited incremental traction or strategic emphasis in the short term.
Product & Innovation
MongoDB acquired Voyage AI for $220M, adding top-tier embedding and reranking models to enhance retrieval accuracy and reduce AI hallucinations. The models rank among the best on Hugging Face and are already used by LangChain, Anthropic, and Harvey.
Voyage AI will be fully integrated into the core MongoDB platform, enabling auto-embedding at the point of data entry. Developers will no longer need to rely on third-party tools for vectorization, storage, and reranking. MongoDB is positioning itself as the default AI-native database, replacing fragmented AI infrastructure with a unified solution.
Vector Search and semantic search are now built directly into the operational database. AI development is simplified through native support for transactional consistency, real-time data access, and enterprise-grade security.
Revenue by Region
The Americas region accounts for 60% of total revenue, making it $MDB MongoDB’s largest market, with revenue growing +21.5% YoY in Q4.
The EMEA region contributes 28% of total revenue and is growing more slowly at +16% YoY.
The Asia Pacific region is the smallest by revenue, but it recorded the highest growth rate at +25% YoY.
Market Leader
$MDB MongoDB was named a Leader in the 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud Database Management Systems for the third consecutive year, reflecting strong innovation, execution, and customer alignment.
In 2024, MongoDB launched MongoDB 8.0, delivering over 30% faster performance, stronger security, and more cost-efficient scaling. The release included hundreds of new features designed to simplify application development and lower operational costs.
The MongoDB AI Applications Program expanded, offering a full-stack AI solution paired with professional services to accelerate deployment. MongoDB was also named the most loved vector database in Retool’s State of AI report for the second straight year.
As a founding member of the U.S. AI Safety Consortium, MongoDB is actively shaping the future of safe and trustworthy AI at the national level.
Customers
$MDB MongoDB added 1,900 total customers, which is in line with the average over the past two years.
The company also added 82 large customers with ARR over $100K, a relatively weak addition, comparable to the level from a year ago, with a growth rate of +17% YoY.
Customer Success Stories
Grab, Southeast Asia’s largest super app, migrated its key Grab Kiosk application to MongoDB Atlas, enabling real-time scalability, improved automation, and enhanced developer efficiency. The shift led to a 50% reduction in time spent on database maintenance, freeing engineering resources to focus on product innovation.
Urban Outfitters modernized its infrastructure using Atlas and the document model, replacing legacy systems that lacked flexibility. This transition supported the rollout of AI-driven personalization and advanced search capabilities across its digital and physical retail footprint.
Swisscom, Switzerland’s leading telecom provider, deployed a GenAI application in just 12 weeks using Atlas to support a RAG-based use case. Unstructured data like reports and recordings were embedded into vector formats to enable high-accuracy contextual retrieval via Vector Search.
The Associated Press, Catalan Department of Health, Zebra Technologies, and Paychex also selected MongoDB to drive modernization and support AI workloads, validating the platform’s role in critical and regulated industries.
Large Customer Wins
MongoDB ended Q4 with 320 customers generating over $1 million in ARR, up 24% YoY, signaling momentum in enterprise adoption. The number of customers spending at least $100K annually rose to 2,396, up from 2,052 last year.
The total customer base reached 54,500, with over 53,100 using Atlas. Growth came from both new accounts and expansion within the existing base, reflecting increased relevance in strategic cloud modernization and AI initiatives.
Large deals included multi-year non-Atlas contracts, contributing more than $10 million above guidance in Q4. MongoDB emphasized that most non-Atlas customers are now deploying incremental workloads on Atlas, driving future upsell potential and cross-platform expansion.
Retention
$MDB MongoDB's Net Dollar Retention (NDR) stands at 118%, down from 120% in the previous quarter, but still above the median of 117% for the SaaS companies I monitor.
Quarterly Performance Highlights
The most important factor for $MDB MongoDB is the growth of Atlas. Atlas's share of revenue grew to 71%.
$MDB Atlas's revenue growth has been gradually slowing, reaching 24% YoY in Q4, though Atlas continues to grow faster than overall company revenue.
Based on the guidance for the next quarter, if the company beats its forecast by 5.7%, as it did in Q4, Q1 growth could reach approximately 30%, indicating a potential acceleration in revenue growth.
MongoDB Atlas Net new ARR
$MDB MongoDB Atlas added $117 million in net new ARR in Q4 2024, which is 14% higher than the same quarter last year.
This is the highest net new ARR ever added by Atlas in the company’s history.
CAC Payback Period and RDI Score
$MDB MongoDB's return on S&M spending deteriorated to 36.2—the CAC Payback Period is high and worse than the median for SaaS companies (the median for the SaaS companies I track is 20.8 months).
The R&D Index (RDI Score) for Q4 stands at 1.11, which is slightly below the median of 1.2 for the SaaS companies I monitor, but significantly higher than the industry median of 0.7.
An RDI Score above 1.4 is generally considered indicative of best-in-class performance. The low industry median of 0.7 highlights the importance of efficient R&D investment.
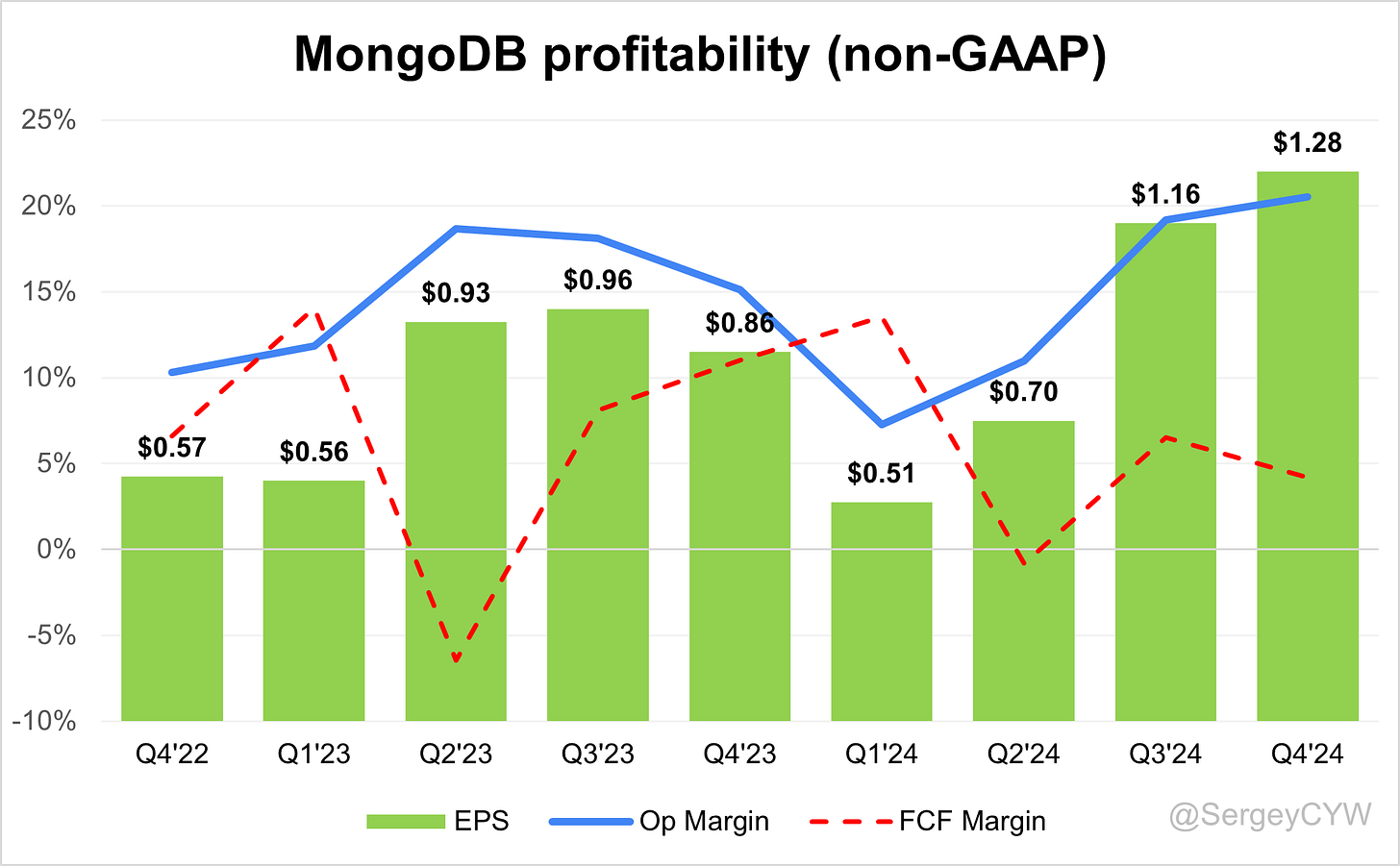
Profitability
Over the past year, $MDB MongoDB's margins have changed:
Gross margin decreased from 77.2% to 75.1%, due to the growing share of Atlas, which is a more cost-intensive offering.
Operating Margin increased from 15.1% to 20.5%.
FCF margin decreased from 11.0% to 4.2%.
Operating expenses
$MDB MongoDB's non-GAAP operating expenses have gradually decreased, primarily due to reduced sales and marketing (S&M) spending, which declined from 41% to 31% of revenue.
R&D expenses remain high at 16%, as the company continues to invest in future growth through product enhancements and updates.
General and administrative (G&A) expenses have also declined, now representing just 7% of revenue.
Balance Sheet
$MDB Balance Sheet: Total debt stands at $74M, while MongoDB holds $2,337M in cash and cash equivalents, exceeding total debt and ensuring a healthy balance sheet.
Dilution
$MDB Shareholder Dilution: MongoDB's stock-based compensation (SBC) expenses have been declining over the past four quarters, reaching 24% of revenue in the last quarter. While this shows progress, it is still relatively high compared to other SaaS companies.
Shareholder dilution increased significantly in Q4, with the weighted-average number of basic common shares outstanding rising 7.3% YoY.
Conclusion
MongoDB provided a strong forecast for Q1, indicating an acceleration in revenue growth, what could confirm this trend of accelerating revenue growth starting from Q2 2024, when revenue growth slowed to just 13%.
In comparison, Snowflake reported Product revenue growth of +27.8% YoY, but based on the guidance for the next quarter, this growth is expected to decelerate.
Meanwhile, MongoDB Atlas revenue grew by +24% YoY in Q4, but is likely to accelerate to 29–30% YoY in the upcoming quarter—potentially overtaking Snowflake’s Product revenue growth.
Leading Indicators
RPO growth of +26.5% outpaced revenue growth.
Billings growth slowed to 17%, which is below revenue growth—a yellow flag.
Atlas Net New ARR additions reached an all-time high, up +17% YoY.
Large customer additions were relatively weak but improved YoY in Q4.
Key Indicators
Net Dollar Retention (NDR) declined 2 percentage points QoQ to 118%.
CAC Payback Period worsened significantly to 36.2 months, which is worse than average.
RDI Score slightly declined to 1.11, but remains around the median compared to other SaaS companies I track.
The forecast implies revenue growth acceleration, supported by strong Atlas Net New ARR additions and RPO growth outpacing revenue. However, weak billings growth and mediocre customer additions should not be overlooked.
From a valuation standpoint, MongoDB appears undervalued compared to other Big Data SaaS companies, currently trading at a discount relative to its Forward EV/Sales multiple.
It’s also important to highlight that MongoDB is not a traditional subscription-based SaaS company. It operates under a consumption-based model, making revenue growth more volatile compared to traditional SaaS. As a result, metrics like RPO and Billings also tend to be more volatile.
MongoDB currently represents 1.8% of my portfolio. I will continue to closely monitor Atlas growth. While management has provided a strong forecast suggesting an acceleration in revenue, I don’t yet see clear confirmation of this trend in the leading and key indicators.
That’s why I’m keeping my position relatively small for now and will reassess after the next quarter. The expected acceleration in MongoDB Atlas growth—potentially surpassing Snowflake Product growth—is encouraging.